AMD FidelityFX™ Single Pass Downsampler (SPD)
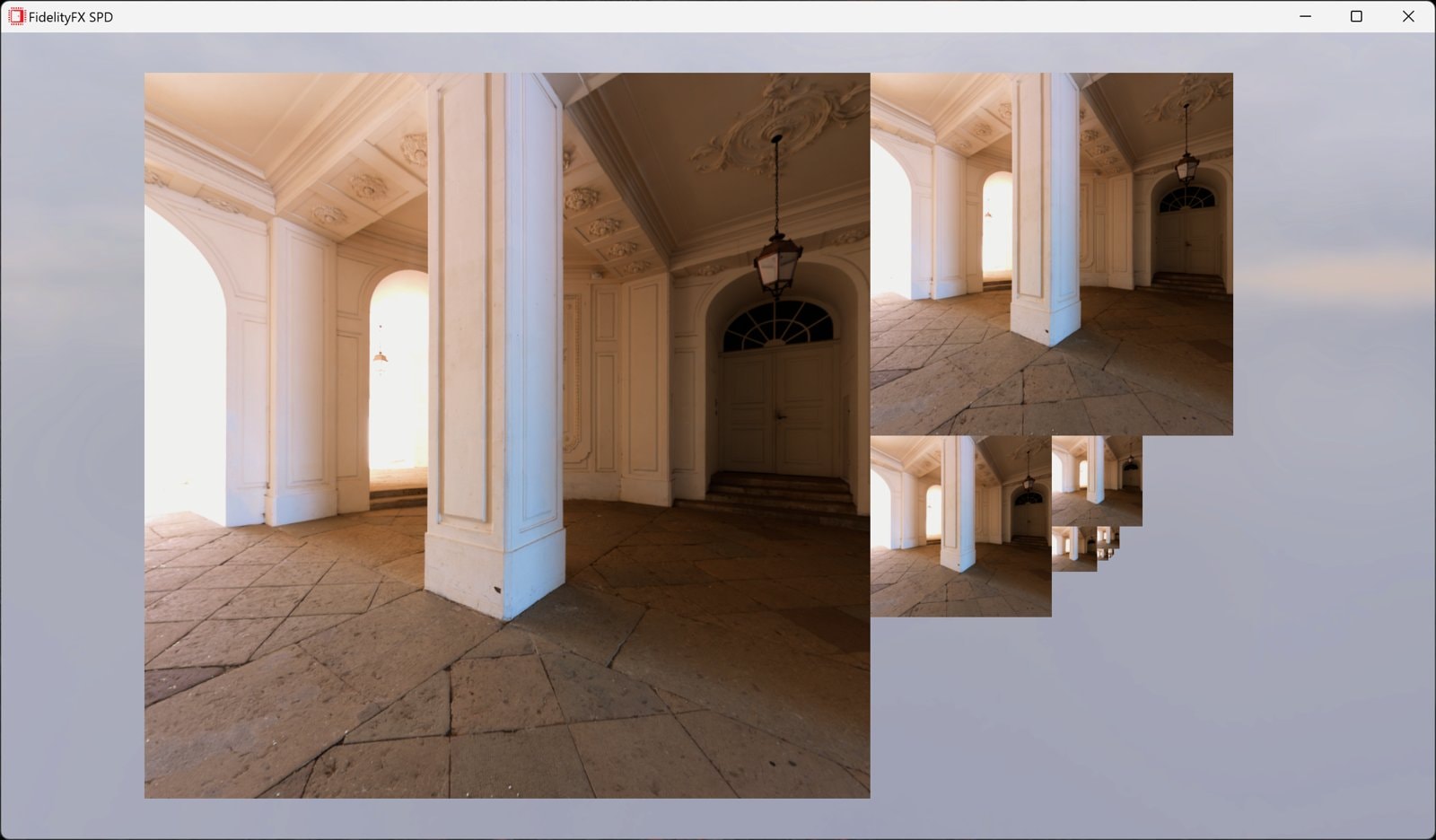
AMD FidelityFX Single Pass Downsampler (SPD) 提供了一个 AMD RDNA™ 架构优化的解决方案,用于生成纹理的最多 12 个 MIP 级别。
MSAA Resolve 与 HDR 混合时的一个常见问题是,一个具有较高 HDR 值的样本会压倒所有其他样本,导致边缘的抗锯齿效果感知不佳。解决此问题的一种方法是使用一个不切实际的巨大滤波器内核,并混合每个像素不切实际的大量样本。
一种实时解决方案是接受 Resolve 中的偏差,并根据样本的亮度降低其权重,从而导致亮边缘在视觉上收缩而不是扩张(如果无偏差则会发生)。此过程等同于先进行色调映射再进行 Resolve,然后在 Resolve 之后反转该色调映射。
本文介绍了一种优化后的技术,该技术是 Brian Karis [Epic] 在 Graphics Rants: Tone mapping 中提到的技术的修改版本。核心改动是用 `max3(red,green,blue)` 替换 `luma` 计算。基于 `luma` 的色调映射器具有基于颜色色调的可变权重,而 `max3` 基础的色调映射器则不具备此特性。 `max3` 基础的色调映射器可以消除相似亮度的混合颜色边缘的色调偏移。
在所有 GCN 版本上,对 `max3()` 的操作都映射为一个指令,即 `v_max3_f32`。Fiji、GCN3 的 GCN 指令集 文档可在此处获取。驱动程序端的 AMD DX 着色器编译器会自动将 `max(x, max(y, z))` 转换为 `max3(x, y, z)`。此功能以及 `min3()` 和 `mid3()` 也通过以下扩展明确暴露于 GLSL 中: AMD_shader_trinary_minmax。
以下是色调映射器及其逆函数的 HLSL 实现。
float max3(float x, float y, float z) { return max(x, max(y, z)); }
// Apply this to tonemap linear HDR color "c" after a sample is fetched in the resolve.// Note "c" 1.0 maps to the expected limit of low-dynamic-range monitor output.float3 Tonemap(float3 c) { return c * rcp(max3(c.r, c.g, c.b) + 1.0); }
// When the filter kernel is a weighted sum of fetched colors,// it is more optimal to fold the weighting into the tonemap operation.float3 TonemapWithWeight(float3 c, float w) { return c * (w * rcp(max3(c.r, c.g, c.b) + 1.0)); }
// Apply this to restore the linear HDR color before writing out the result of the resolve.float3 TonemapInvert(float3 c) { return c * rcp(1.0 - max3(c.r, c.g, c.b)); }以及一个 GLSL Shadertoy 示例: https://www.shadertoy.com/view/Xdd3Rr
以下是一个在使用上述函数进行低质量 4xMSAA 盒式滤波器 Resolve 的示例,
return TonemapInvert( TonemapWithWeight(sample0, 0.25) + TonemapWithWeight(sample1, 0.25) + TonemapWithWeight(sample2, 0.25) + TonemapWithWeight(sample3, 0.25));这是另一个示例,这次是一个完整的 HLSL 着色器,不包含 `TonemapInvert()`,这是一个随机的 5 抽头水平滤波器。
float max3(float x, float y, float z) { return max(x, max(y, z)); }
float3 TonemapWithWeight(float3 c, float w) { return c * (w * rcp(max3(c.r, c.g, c.b) + 1.0)); }
Texture2D tex0;SamplerState smp0;
float3 main(float2 pos : TEXCOORD) : SV_Target { return TonemapWithWeight(tex0.SampleLevel(smp0, pos, 0, int2(-2,0)), 0.1) + TonemapWithWeight(tex0.SampleLevel(smp0, pos, 0, int2(-1,0)), 0.2) + TonemapWithWeight(tex0.SampleLevel(smp0, pos, 0, int2( 0,0)), 0.4) + TonemapWithWeight(tex0.SampleLevel(smp0, pos, 0, int2( 1,0)), 0.2) + TonemapWithWeight(tex0.SampleLevel(smp0, pos, 0, int2( 2,0)), 0.1); }在 Shader Analyzer (GPU Perf Studio 的一部分) 中检查此着色器的反汇编,可以看到第一个抽头之后的每个滤波器抽头对应的 GCN 指令如下。
v_max3_f32v_add_f32v_rcp_f32 <--- rcp takes 4x the runtime as other VALU (vector ALU) operationsv_mul_f32 <--- folds the scalar filter weight to the tonemap weight before multiply by the color---------v_mac_f32 <--- multiply by weight and accumulate with the weighted sumv_mac_f32 <--- multiply by weight and accumulate with the weighted sumv_mac_f32 <--- multiply by weight and accumulate with the weighted sum应用可逆色调映射器后,每个滤波器抽头的额外成本仅为顶部的 4 条指令,耗时 7 个 VALU 操作。滤波器的每个抽头总共需要 10 个 VALU 操作。以 Fiji Nano 为例,根据峰值规格,在 1 毫秒内可处理约 4 亿个此类滤波器抽头(实际测量值取决于源抽头所需的带宽等)。