
将《底特律:变人》从 PlayStation® 4 移植到 PC – 第一部分
将 PS4® 游戏《底特律:变人》移植到 PC 带来了一些有趣的挑战。这是 Quantic Dream 和 AMD 工程师之间合作的第一部分,讨论了使用 Vulkan® 的决定,并探讨了着色器管线和描述符。

这是一个三部分系列文章,由 Quantic Dream 的 3D 引擎总监 Ronan Marchalot、3D 引擎高级开发者 Nicolas Vizerie 和 Jonathan Siret,以及 AMD 的开发者技术工程师 Lou Kramer 联合撰写。
博客中包含的信息代表 AMD 或第三方作者在发布日期当时的观点。博客文章包含作者的个人意见,可能不代表 AMD 的立场、策略或观点。AMD 和/或第三方作者无义务更新任何前瞻性内容。GD-84
您好,欢迎阅读我们关于将《底特律:变人》从 PS4 移植到 PC 系列的第二部分。在第一部分中,Quantic Dream 的 Ronan Marchalot 解释了他们决定使用 Vulkan® 的原因,并讨论了着色器管线和描述符。在第二部分中,AMD 的 Lou Kramer 将讨论 PC 上特别是 AMD 显卡的非统一资源索引。
扩展程序 VK_EXT_descriptor_indexing 已成为 Vulkan® 1.2 的核心部分。此扩展允许应用程序在着色器中选择具有动态(非统一)索引的描述符集。非统一意味着索引在整个子组中可以具有不同的值。
例如,在 RDNA 上,子组的大小为 32 或 64。子组中的所有线程,也称为车道(lanes),在单个 SIMD 单元上并行执行。统一变量存储在标量寄存器中,所有车道只有一个值。非统一变量存储在向量寄存器中,为每个车道单独存储一个值。
默认情况下,访问数组中资源的索引被认为是统一的。我们来看下面的例子:
// the descriptor set, an array of 13 resources (textures)[[vk::binding(0)]] RWTexture2D imgDst[13] :register(u0);
// the threadgroup has 128 lanes so there are in total either 4 or 2 subgroups// (of size 32 or respectively of size 64)[numthreads(64,2,1)]
void main(uint3 LocalThreadId : SV_GroupThreadID){ // the index that will be used to access an element in the descriptor set uint index = 0;
// load instruction for the texture at index 0 float4 value = imgDst[index].Load(LocalThreadId.xy);
// store instruction for the texture at index 1 imgDst[index + 1][LocalThreadId.xy] = value;}变量 index 的值在单个子组中的所有车道上都是统一的。在这个简单的例子中,它是 0,显然是统一的。
为了进行案例研究,我们来看一下着色器编译器如何处理这类代码。具体来说,Radeon 驱动程序 20.5.1 在 Radeon RX 5700 XT 上的着色器编译器生成的 ISA 如下:
注意:不用担心,您不必理解每一行!此外,本文中呈现的所有 ISA 均基于上述相同的驱动程序和 GPU。使用不同的驱动程序和 GPU 时,可能会有所不同。
s_inst_prefetch 0x3s_getpc_b64 s[0:1]s_mov_b32 s0, s2
// here we load the descriptor for the texture we want to access:// the descriptor of texture[0] is loaded to scalar registers s[4:11]// the descriptors are always stored in scalar registers// and thus, are uniform across all laness_load_dwordx8 s[4:11], s[0:1], 0x0s_waitcnt lgkmcnt(0)
// we load from descriptor stored at s[4:11] -> points to texture[0]image_load v[2:5], v[0:1], s[4:11] dmask:0xf dim:SQ_RSRC_IMG_2Dv_nop
// we load the descriptor of texture[1] into s[0:7]s_load_dwordx8 s[0:7], s[0:1], 0x20s_waitcnt vmcnt(0) lgkmcnt(0)
// we write into texture[1]image_store v[2:5], v[0:1], s[0:7] dmask:0xf dim:SQ_RSRC_IMG_2D unorm glcs_endpgm在上面的示例中,index 被赋值为一个常量,该常量始终是统一的。
但是,如果我们不为 index 分配一个常量值呢?我们来看下面的例子:
[[vk::binding(0)]] RWTexture2D imgDst[13] :register(u0);[numthreads(64,2,1)]
void main(uint3 LocalThreadId : SV_GroupThreadID){ uint index = LocalThreadId.y; float4 value = imgDst[index].Load(LocalThreadId.xy); imgDst[index + 1][LocalThreadId.xy] = value;}请记住,根据规范,index 仍然必须是统一的——所以它在单个子组中的每个车道上都具有相同的值。这个例子中是真的吗?
LocalThreadId.xy 在车道之间可能不同。但是,在 AMD GPU 上,计算着色器的车道索引模式是行主序的。这意味着,一个线程组有四个子组,车道索引为 [0,31][0];[32,63][0];[0,31][1];[32,63][1],或者有两个子组,车道索引为 [0,63][0];[0,63][1]。因此,LocalThreadId.y 在一个子组中是统一的。
大小为 32 的子组中的车道索引
[0, 31][0] | [32,63][0] |
[0, 31][1] | [32,63][1] |
大小为 64 的子组中的车道索引
[0, 63][0] |
[0, 63][1] |
每个单元格是一个子组,索引为 [x][y]。请注意,对于 y,每个子组只有一个可能的值,因为 y 在单个子组的所有车道上都是统一的。
由于规范要求索引必须是统一的,编译器可以将 index 视为统一的,而无需进一步确认。编译器可以假定代码符合规范。因此,编译器可以根据 index 是统一的事实生成 ISA。
ISA 如下:
s_inst_prefetch 0x3s_getpc_b64 s[0:1]
// only load the value of gl_LocalInvocationID.y of the first active lane// as index is considered a uniform value, it must be equal across all lanes// store it in a scalar registerv_readfirstlane_b32 s0, v1s_mov_b32 s3, s1s_lshl_b32 s0, s0, 5
// load the texture descriptor from texture[gl_LocalInvocationID.y-from-first-lane]s_load_dwordx8 s[4:11], s[2:3], s0s_add_u32 s0, s0, 32s_waitcnt lgkmcnt(0)image_load v[2:5], v[0:1], s[4:11] dmask:0xf dim:SQ_RSRC_IMG_2Dv_nops_load_dwordx8 s[0:7], s[2:3], s0s_waitcnt vmcnt(0) lgkmcnt(0)image_store v[2:5], v[0:1], s[0:7] dmask:0xf dim:SQ_RSRC_IMG_2D unorm glcs_endpgm请注意 readFirstLane 的用法——用于访问纹理数组的索引被加载为统一值。这完全没问题,因为我们知道 index 实际上是统一的。但是,当我们更改线程组 xy 时会发生什么?
[numthreads(16,8,1)]现在,LocalThreadId.y 对于每个子组来说是非统一的——线程组中子组的车道索引是:
[0, 15][0, 1] | [0, 15][2, 3] | [0, 15][4, 5] | [0, 15][6, 7] |
然而,生成的 ISA 仍然与上面相同,它不依赖于线程组的大小——因此,最终输出将是不正确的!要解决此问题,我们必须添加 NonUniformResourceIndex 关键字(或 GLSL 中的 nonuniformEXT 关键字)。
添加 NonUniformResourceIndex 关键字后,代码如下:
[[vk::binding(0)]] RWTexture2D imgDst[13] :register(u0);[numthreads(16,8,1)]
void main(uint3 LocalThreadId : SV_GroupThreadID){ uint index = LocalThreadId.y; float4 value = imgDst[NonUniformResourceIndex(index)].Load(LocalThreadId.xy); imgDst[NonUniformResourceIndex(index + 1)][LocalThreadId.xy] = value;}生成的 ISA 更为复杂,因为编译器不能再假设 index 的值是统一的,而且这也不是像我们最初分配 index 给常量值那样显而易见的情况。
s_inst_prefetch 0x3s_getpc_b64 s[0:1]s_mov_b32 s0, s2v_lshlrev_b32_e32 v2, 5, v1s_mov_b32 s2, exec_los_mov_b32 s3, exec_los_nop 0s_nop 0
_L2: // we still have readfirstlane here, the descriptor is loaded in // scalar registers. We can’t pick different descriptors // in parallel, but must pick them one by one v_readfirstlane_b32 s4, v2
// check if we picked the right descriptor for the lane // if yes, load from the texture at the picked descriptor v_cmp_eq_u32_e32 vcc_lo, s4, v2 s_and_saveexec_b32 s5, vcc_lo
// if not right descriptor, skip imageLoad s_cbranch_execz _L0
BBF0_0: s_load_dwordx8 s[8:15], s[0:1], s4 s_waitcnt vmcnt(0) lgkmcnt(0) s_waitcnt_depctr 0xffe3 image_load v[3:6], v[0:1], s[8:15] dmask:0xf dim:SQ_RSRC_IMG_2D s_andn2_b32 s3, s3, exec_lo
// if we picked right descriptor for the lane, // jump to the imageStore part s_cbranch_scc0 _L1
_L0: // if it was the wrong descriptor, jump back to the beginning // and pick the descriptor of the first remaining active lane // loop goes on until no active lanes are remaining for the // imageLoad instruction v_nop s_mov_b32 exec_lo, s5 s_and_b32 exec_lo, exec_lo, s3 s_branch _L2
_L1: v_nop s_mov_b32 exec_lo, s2 v_add_nc_u32_e32 v2, 32, v2 s_mov_b32 s2, exec_lo s_nop 0 s_nop 0 s_nop 0 s_nop 0
_L5: // do again a ‘waterfall’ loop as before, but now for the descriptors // used for the imageStore instruction v_readfirstlane_b32 s3, v2 v_cmp_eq_u32_e32 vcc_lo, s3, v2 s_and_saveexec_b32 s4, vcc_lo s_cbranch_execz _L3
BBF0_1: s_load_dwordx8 s[8:15], s[0:1], s3 s_waitcnt vmcnt(0) lgkmcnt(0) s_waitcnt_depctr 0xffe3 image_store v[3:6], v[0:1], s[8:15] dmask:0xf dim:SQ_RSRC_IMG_2D unorm glc s_andn2_b32 s2, s2, exec_lo s_cbranch_scc0 _L4
_L3: v_nop s_mov_b32 exec_lo, s4 s_and_b32 exec_lo, exec_lo, s2 s_branch _L5
_L4: s_endpgm这里发生了什么?编译器会添加逻辑来迭代所有车道,直到每个车道都具有正确的索引。这也称为“瀑布”,如果您偶然遇到这个术语的话 😊
对于每个唯一的索引,我们将经历一次额外的循环迭代。在 [numthreads(16,8,1)] 的情况下,我们需要两次迭代来涵盖所有情况。例如,对于第一个线程组,一次迭代用于 LocalThreadId.y == 0,另一次迭代用于 LocalThreadId.y == 1。
对于 [numthreads(64,2,1)] 的线程组大小的情况,实际上只有一次迭代。
上述两种情况都使用上面生成的 ISA 产生了正确的输出,但是对于 [numthreads(64,2,1)],迭代不同 index 值的逻辑是不必要的,因为每个子组只有一个可能的 index 值。
要删除循环,编译器必须提前知道每个子组只有一个唯一的 index 值。这样做的复杂性取决于具体情况。此外,还有一些情况,编译器根本无法确定一个值是统一的还是非统一的。
到目前为止的要点如下:
在需要的地方添加非统一限定符,否则您可能会看到损坏或其他不良情况发生。对于非统一索引,缺少 NonUniformResourceIndex 关键字是违反规范的。
向所有纹理访问添加非统一限定符可能会在某些硬件上显著降低性能。
在片段着色器中,需要确定正确细节级别(Level of Detail)或使用各向异性过滤的纹理访问,依赖于计算隐式导数。导数是根据当前图元(primitive)的 2×2 片段着色器组(一个**四边形**)中的值计算的。
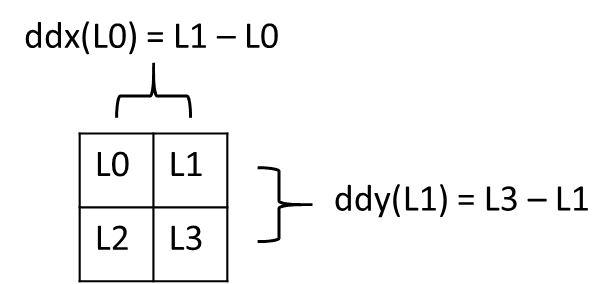
不幸的是,根据当前的 Vulkan®(和 DirectX®)API 规范,并未实际保证用于确定导数的**四边形**是哪一个,它只需对正在渲染的当前图元保持准确即可。如果采样指令在图元内的统一控制流中未被调用,则导数是未定义的。
为确保导数是定义的,采样指令必须始终在绘制的完全统一的控制流中调用,或者在仅基于图元 ID 和统一值的条件内调用。
当资源数组的索引非统一时,也会出现类似的问题。实现可以自由地假设正在访问的资源是统一索引的,如果不是,则访问无效。在 AMD 的当前实现中,这将导致采样指令返回未定义的值。
struct VERTEX{ [[vk::location(0)]] float2 vTexcoord : TEXCOORD; [[vk::location(1)]] uint inIndex : INDEX;};
[[vk::binding(1)]] Texture2D imgDst[13] :register(t0);[[vk::binding(1)]] SamplerState srcSampler :register(s0);
[[vk::location(0)]] float4 main(VERTEX input) : SV_Target{ return imgDst[NonUniformResourceIndex(input.inIndex)].Sample(srcSampler, input.vTexcoord);}


